These Class 10 AI Important Questions Chapter 7 Evaluation Class 10 Important Questions and Answers NCERT Solutions Pdf help in building a strong foundation in artificial intelligence.
Evaluation Class 10 Important Questions
Class 10 AI Evaluation Important Questions
Important Questions of Evaluation Class 10 – Class 10 Evaluation Important Questions
Evaluation Class 10 Subjective Questions
Question 1.
Is high accuracy equivalent to good performance?
Answer:
High accuracy is not equivalent to good performance, especially in cases where the dataset is imbalanced or the cost of false positives and false negatives is different. Evaluating a model’s performance requires considering a variety of metrics such as precision, recall, F1 score, specificity, and ROC-AUC to get a comprehensive understanding of its effectiveness.
Examples of Misleading High Accuracy
1. Fraud Detection If only 1 % of transactions are fraudulent, a model that always predicts “not fraud” will have 99 % accuracy but will fail to detect any fraudulent transactions.
2. Medical Diagnosis For a disease affecting 2% of the population, a model predicting “no disease” for everyone achieves 98% accuracy but fails to identify any actual cases of the disease.
Question 2.
How much percentage of accuracy is reasonable to show good performance?
Answer:
The percentage of accuracy that signifies good performance depends on the specific context and application. In some fields like image classification, accuracy above 90% might be considered excellent, whereas in fraud detection or medical diagnostics, even higher thresholds might be required due to the critical nature of the decisions made. Therefore, what constitutes a reasonable percentage of accuracy for good performance varies widely and should be evaluated relative to the consequences of both types of prediction errors in the specific domain.
![]()
Question 3.
Is good Precision equivalent to a good model performance? Why?
Answer:
No, good Precision alone is not equivalent to good model performance. Precision is a measure of how many of the predicted positive cases are actually positive (True Positives out of all predicted positives). While high Precision indicates that the model is good at avoiding false positives, it does not consider the model’s ability to identify all relevant cases (True Positives) in the dataset.
A good model performance should be evaluated comprehensively, considering other metrics such as Recall, F1-score, and possibly domain-specific metrics that are relevant to the specific problem being addressed. Therefore, a good model performance requires a balanced consideration of Precision along with other metrics to assess its overall effectiveness and suitability for the intended application.
Question 4.
Which one do you think is better? Precision or Recall? Why?
Answer:
There isn’t a single “better” metric between precision and recall. They both offer valuable but distinct insights into a model’s performance.
Precision focuses on the positive predictions: how many of those the model classified as positive actually belong to the positive class. It reflects how good the model is at avoidìng false positives.
Recall concentrates on capturing all positive cases: how well the model identifies all actual positive instances. It highlights how good the model is at avoiding false negatives.
The best choice depends on the specific problem you’re tackling. In some cases, minimizing false positives might be crucial (e.g., a spam filter), while in others, finding all positive cases is essential (e.g., a medical diagnosis).
Question 5.
Give example of high false negative cost.
Answer:
Example of High False Negative Cost:
Medical diagnosis Imagine a model predicting a disease. A false negative occurs when the model incorrectly predicts someone is healthy when they actually have the disease.
This can lead to delayed treatment and worse health outcomes. In this case, accuracy might not be the best metric. We want to minimize the number of false negatives, even if it means sacrificing some accuracy.
![]()
Question 6.
Give example of high false positive cost.
Answer:
Example of High False Positive Cost
Spam filter: A spam filter incorrectly identifies a legitimate email as spam (false positive). This can lead to important emails being missed.
While accuracy is important, a high false positive rate can be frustrating for users. In this case, we might prioritize a model that minimizes incorrectly flagging real emails.
Evaluation Class 10 Very Short Type Answer Questions
Question 1.
With reference to evaluation process of understanding the reliability of any AI model, define the term True Positive.
Answer:
True Positive refers to the instances where the model correctly identifies the positive class or outcome.
Question 2.
Give an example where high precision is not useful.
Answer:
Too many false negative will make the spam filter in effective but false positive may cause important mails to be must and hence precession is not usable.
Question 3.
What is Recall?
Answer:
Recall refers to the ability of a model to correctly identify all relevant instances from a dataset.
Question 4.
Define accuracy.
Answer:
Accuracy is a measure of the overall correctness of a model’s predictions. It represents the proportion of correct predictions out of the total number of predictions made by the model.
![]()
Question 5.
In which form confusion matrix is recorded?
Answer:
The confusion matrix is recorded in tabular form, typically with actual class labels represented by rows and predicted class labels represented by columns.
Question 6.
Give one reason for the inefficiency of the AI model.
Answer:
AI model could be insufficient or low-quality training data. If the model is not trained on a diverse and representative dataset, it may fail to generalise well to unseen data, leading to poor performance and inefficiency.
Question 7.
Give the formula for calculating Precision.
Answer:
Precision = \(\frac{True Positives {True Positives + False Positives \)
Question 8.
Why should we avoid using the training data for evaluation?
Answer:
This is because our model will simply remember the whole training set, and will therefore always predict the correct label for any point in the training set.
Question 9.
What should be the value of F1 score if the model needs to have 100% accuracy?
Answer:
The model will have an F1 score of 1 if it has to be 100 % accurate.
![]()
Question 10.
Which evaluation parameter takes into consideration all the correct predictions?
Answer:
Accuracy
Evaluation Class 10 Short Type Answer Questions
Question 1.
With reference to evaluation stage of Al project cycle, explain the term Accuracy. Also give the formula to calculate it.
Answer:
In the evaluation stage of an AI project cycle, accuracy is a key metric used to assess the performance of a machine learning model. It measures the proportion of correctly classified instances out of all instances examined. In other words, accuracy indicates how often the model is correct in its predictions.
Accuracy = \(\frac{(TP+TN){(TP+TN+FP+FN)\) × 100
Question 2.
What is F1 Score in Evaluation?
Answer:
Fl score can be defined as the measure of balance between precision and recall.
F1 Score = 2 × \(\frac{Precision × Recall {Precision + Recall \)
Question 3.
Give an example of a situation where in false positive would have a high cost associated with it.
Answer:
Let us consider a model that predicts that a mail is spam or not. If the model always predicts that the mail is spam, people would not look at it and eventually might lose important information. Here False Positive condition (Predicting the mail as spam while the mail is not spam) would have a high cost.
Question 4.
What is a confusion matrix? What is it used for?
Or
Define Confusion Matrix.
Answer:
The confusion matrix is used to store the results of comparison between the prediction and reality. From the confusion matrix, we can calculate parameters like recall, precision, F1 score which are used to evaluate the performance of an AI model.
Question 5.
Draw the confusion matrix for the following data
The number of true positive = 100
The number of true negative 47
The number of false positive = 62
The number of false negative = 290
Answer:
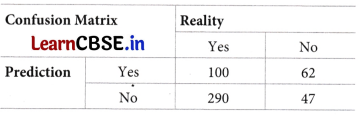
Question 6.
People of a village are totally dependent on the farmers for their daily food items. Farmers grow new seeds by checking the weather conditions every year. An Al model is being deployed in the village which predicts the chances of heavy rain to alert farmers which helps them in doing the farming at the right time. Which evaluation parameter out of precision, recall and F1 Score is best to evaluate the performance of this AI model? Explain.
Answer:
Let us take each of the factor into consideration at once,
If precision is considered, FN cases will not be taken into account, so it will be of great loss as if the machine will predict there will be no heavy rain, but if the rain occurred, it will be a big monetary loss due to damage to crops.
If only recall is considered, then FP cases will not be taken into account. This situation will also cause a big amount of loss, as all people of the village are dependent on farmers for food, and if the model predicts there will be heavy rain and the farmers may not grow crops, it will affect the basic needs of the people.
Hence F1 Score is the best suited parameter to test this AI model, which is the balance between Precision and Recall.
Evaluation Class 10 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Traffic Jams have become a common part of our lives nowadays. Living in an urban area means you have to face traffic each and every time you get out on the road. Mostly, school students opt for buses to go to school. Many times, the bus gets late due to such jams and the students are not able to reach their school on time. Thus, Al model is created to predict explicitly if there would be traffic jam on their way to school or not. The Confusion Matrix for the same is:
| The Confusion Matrix | Actual 1 | Actual 0 |
| Predicted 1 | 50 | 50 |
| Predicted 0 | 0 | 0 |
Explain the process of evaluating F1 score for the given problem.
Answer:
From the confusion matrix provided:
Now, let’s calculate the precision, recall, and F1 score:

Question 2.
Automated trade industry has developed an Al model which predicts the selling and purchasing of automobiles during testing the AI model game with the following predictions.

(a) How many total tests have been performed in the above scenario?
(b) Calculate precision, recall and F1 score.
Answer:
From the confusion matrix:
TP = 60
FP = 25
TN = 10
FN = 5
(a) Total tests performed: The total number of tests is the sum of all entries in the confusion matrix:
Total tests = TP + FP + TN + FN
= 60 + 25 + 10 + 5 = 100
(b) Now, let’s calculate precision, recall and F1 score:
1. Precision (P) = TP /(TP+FP)
2. Recall (R)
3. F1 Score = 2 ×(P × R) /(P+R)
= 60 /(60+25)
= 60 / 85 = 0.706
= TP /(TP+FN)
= 60 /(60+5)
= 60 / 65 = 0.923
= 2 × (P × R) /(P+R)
= 2 × (0.706 × 0.923) /(0.706+0.923)
= 2 × (0.651 / 1.629)
= 2 × 0.399
= 0.799
![]()
Question 3.
Imagine that you have come up with an AI based prediction model which has been deployed on the roads to check traffic jams. Now, the objective of the model is to predict whether there will be a traffic jam or not. Now, to understand the efficiency of this model, we need to check if the predictions which it makes are correct or not. Thus, there exist two conditions which we need to ponder upon: Prediction and Reality.
Traffic Jams have become a common part of our lives nowadays. Living in an urban area means you have to face traffic each and every time you get out on the road. Mostly, school students opt for buses to go to school. Many times, the bus gets late due to such jams and the students are not able to reach their school on time.
Considering all the possible situations make a Confusion Matrix for the above situation.
Answer:
Case 1: Is there a traffic Jam?
Prediction: Yes Reality: Yes
True Positive
Case 2: Is there a traffic Jam?
Prediction: No Reality: No
True Negative
Case 3: Is there a traffic Jam?
Prediction: Yes Reality: No
False Positive
Case 4: Is there a traffic Jam?
Prediction: No Reality: Yes
False Negative

Question 4.
Take a look at the confusion matrix:

How do you calculate F1 score?
Answer:
We begin the calculation by first using the formula to calculate Precision
Precision is defined as the percentage of true positive cases versus all the cases where the prediction is true. That is, it takes into account the True Positives and False Positives.

Next, we calculate recall as the fraction of positive cases that are correctly identified.

Finally, we calculate the F1 score as the measure of balance between precision and recall.
![]()
Question 5.
An Al model made the following sales prediction for a new mobile phone which they have recently launched:

(i) Identify the total number of wrong predictions made by the model.
(ii) Calculate precision, recall and F1 Score.
Answer:
(i) The total number of wrong predictions made by the model is the sum of false positive and false negative.
FP + FN = 40 + 12 = 52
(ii) Precision = TP/(TP +FP)
= 50 /(50 + 40) = 50 / 90 = 0.55
Recall = TP/(TP+FN)
= 50 /(50+12) = 50 / 62 = .81
F1 Score = 2 × Precision × Recall /(Precision + Recall )
= 2 × 0.55 × .81 /(.55+.81)
= .891 / 1.36 =0.65
The post Evaluation Class 10 Questions and Answers appeared first on Learn CBSE.
from Learn CBSE https://ift.tt/C4gZPsU
via IFTTT
No comments:
Post a Comment